

Deliver superior results against infection vs standard of care (SOC)
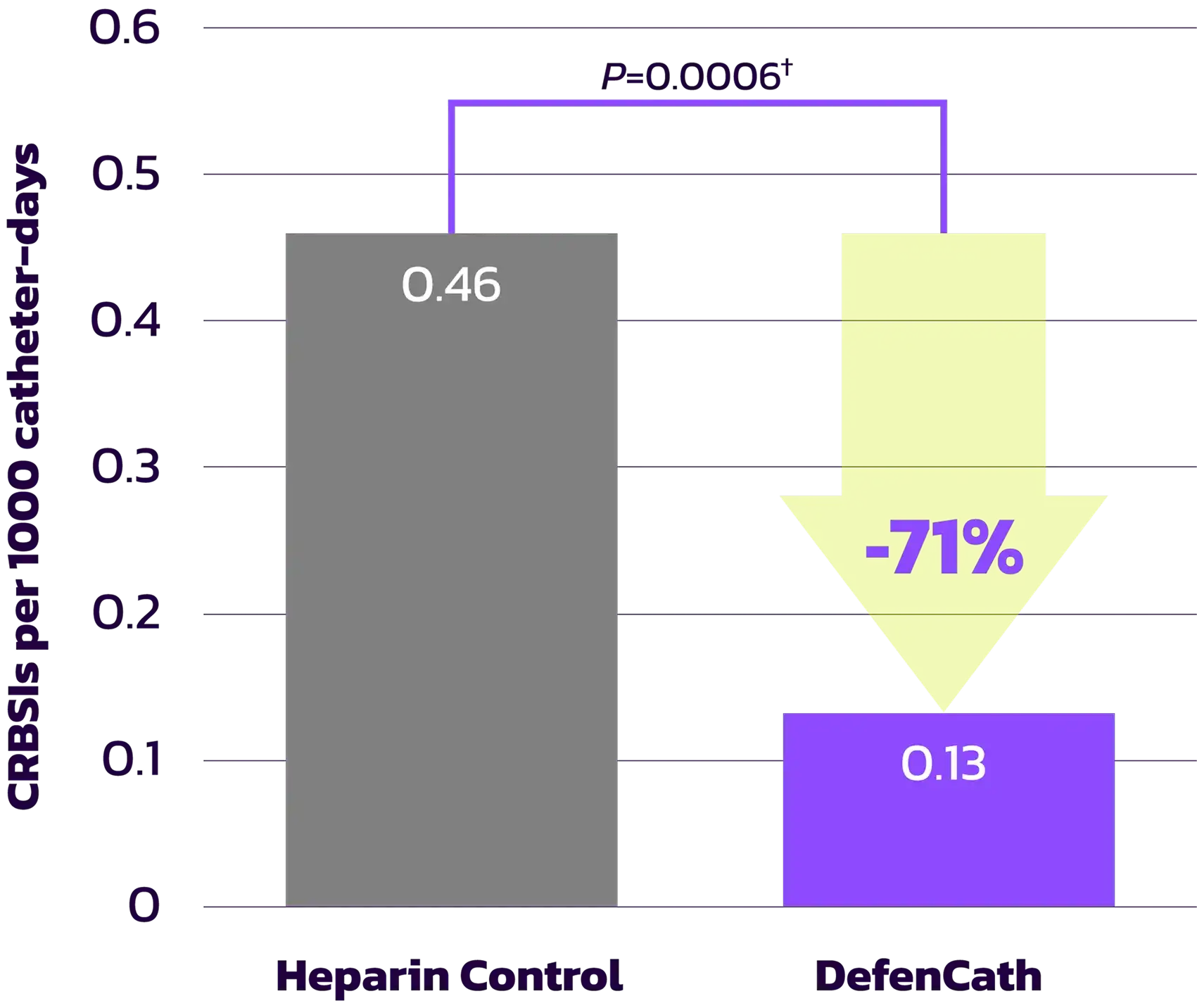
DefenCath significantly improves upon the SOC (heparin) by reducing the risk of catheter‑related bloodstream infections (CRBSIs) by 71%.1,2
LOCK-IT-100
In adult patients with kidney failure receiving chronic hemodialysis (HD) through a central venous catheter (CVC), significant reduction in catheter‑related bloodstream infection (CRBSI) incidence was demonstrated in this trial1
Reduction of CRBSI Risk by 71% 1
Primary Endpoint Results
| DefenCath N=397 | Heparin Control N=398 | |
|---|---|---|
| CAC-adjudicated CRBSI | 9 (2.3%) | 32 (8.0%) |
| Event rate per 1000 catheter-days (95% CI) | 0.13 (0.07, 0.26) | 0.46 (0.33, 0.66) |
| Risk reduction (95% CI)* | 71% (38%, 86%) | |
| Log-rank test P-value | 0.0006 | |
*Based on 1 - Hazard Ratio | ||
 | ||
†Based on Log-rank test | ||
scroll for more
Primary EndpointTime to CRBSI occurrenceCRBSI over time: Proportion of patients without CRBSIs3
†DefenCath contains 13.5 mg/mL of taurolidine and 1,000 USP Units/mL of heparin, as a sterile, non-pyrogenic, pre-mixed, preservative-free, clear, aqueous solution of taurolidine and heparin with a pH of 5.5-6.5.1
‡Control composition: heparin sodium USP 1,000 units/mL, benzyl alcohol 9.45 mg/mL and sodium chloride 9.0 mg/mL.1
| DefenCath (n=397) | Heparin control (n=398) | |
|---|---|---|
| CAC-adjudicated CRBSI | 9 (2.3%) | 32 (8.0%) |
| Event rate per 1000 catheter-days (95% CI) | 0.13 (0.07, 0.26) | 0.46 (0.33, 0.66) |
| Risk reduction (95% CI)§ | 71% (38%, 86%); P=0.0006* | |
| §Based on 1 — Hazard Ratio. *Log-rank test P-value | ||
| DefenCath (n=398) n (%) | Heparin control (n=399) n (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Loss of Catheter Patency | 63 (16) | 48 (12) |
| Use of Thrombolytic Agenta | 46 (12) | 33 (8) |
| Catheter Removalb | 28 (7) | 26 (7) |
| Catheter Removal without Thrombolytic Agent Use | 17 (4) | 15 (4) |
a11 subjects in each arm had catheter removal following thrombolytic agent use and are included under both categories of use of a thrombolytic agent and catheter removal. b Catheter removal refers to catheters removed due to loss of catheter patency. Overall, a total of 236 patients in the DefenCath arm and 225 patients in the heparin arm had a catheter removal for any reason, including loss of catheter patency. | ||

DEFENCATH TRIAL DESIGN
LOCK-IT-100 was the largest randomized, double blind study of catheter lock solutions (CLS) in the US to date1,3
DefenCath was studied in 795 patients in the pivotal Phase 3 LOCK-IT-100 trial—a randomized, double-blind, active-controlled, multicenter trial.1,3
Study design
The efficacy and safety of DefenCath for reducing the incidence of catheter-related bloodstream infections (CRBSIs) in adult patients with kidney failure receiving chronic hemodialysis (HD) was evaluated in LOCK-IT-100, a randomized, double-blind, active-controlled, multicenter trial.1
A total of 806 patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either DefenCath (taurolidine [13.5 mg/mL], and heparin [1,000 USP Units/mL] [n=397]) or heparin (heparin sodium USP 1,000 units/mL, benzyl alcohol 9.45 mg/mL and sodium chloride 9.0 mg/mL [n=398]) as a catheter lock solution (CLS) and enrollment was not limited to patients with specific types of HD catheters. DefenCath or heparin was instilled into central venous HD catheters at the end of all dialysis sessions and was withdrawn prior to the initiation of the next dialysis session.1
Patient population1
- The median age of patients was 63 years (range, 21-94 years)
- 58% identified as males
- 63% identified as white
- The majority of patients (98%) had HD treatment 3 times per week, and 48% had their catheter implanted within 3 months prior to randomization
In LOCK-IT-1001:
A clinical adjudication committee (CAC) assessed the cases of CRBSI. The CAC definition for CRBSI included one positive blood culture (other than for coagulase-negative staphylococci, which required a confirmatory culture) from a peripheral site or either the arterial or venous catheter hub or the arterial or venous dialysis blood line and the patient had to have signs and symptoms of infection and no other apparent source of bloodstream infection.
PATIENT POPULATION
LOCK-IT-100 participants represented a large and diverse chronic HD-CVC patient population reflective of real‑world patients in the US1,3
Key inclusion criteria3:
- Ages ≥18 years
- Underwent hemodialysis ≥2 times per week in an outpatient HD unit
- Catheters were required to be in place for ≥14 days
- Catheters had to have been used successfully to dialyze the participant ≥2 times prior to enrollment
Key exclusion criteria3:
- Treatment with antibiotics ≤14 days of enrollment
- Catheter exit-site infection
- Thrombolytic treatment (i.e., tissue plasminogen activator [tPA]) in the patient’s current catheter ≤30 days of randomization, or
- Systemic immunosuppression (e.g., patients actively on immunosuppressants), or
- Malignancy with life expectancy ≤6 months
| Characteristic | DefenCath (n=403) | Heparin control (n=403) |
|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD), years | 61 (14) | 61 (14) |
| Age category, years, n (%) | ||
| <65 years | 239 (59) | 236 (59) |
| ≥65 to <75 years | 99 (25) | 95 (24) |
| ≥75 | 65 (16) | 72 (18) |
| Female, n (%) | 184 (46) | 154 (38) |
| Race, n (%) | ||
| American Indian or Alaska Native | 3 (1) | 2 (<1) |
| Asian | 15 (4) | 18 (4) |
| Black or African-American | 126 (31) | 112 (28) |
| Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander | 10 (2) | 4 (1) |
| White | 248 (62) | 262 (65) |
| Other | 1 (0.2) | 5 (1) |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | ||
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 226 (56) | 214 (53) |
| Hispanic or Latino | 177 (44) | 189 (47) |
| BMI, mean (SD), kg/m2,a | 29.7 (7.9) | 29.2 (10.3) |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 278 (69) | 277 (69) |
| Time since first dialysis, monthsb | ||
| Mean (SD) | 21.2 (37.5) | 19.8 (37.0) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0.2, 280.2 | 0.1, 254.8 |
| Time receiving dialysis, n (%) | ||
| ≤30 days | 35 (9) | 31 (8) |
| 1-12 months | 237 (59) | 246 (61) |
| >12 months | 131 (33) | 126 (31) |
| Catheter location, n (%) | ||
| Jugular vein | 371 (92) | 365 (91) |
| Subclavian vein | 30 (7) | 31 (8) |
| Otherc | 2 (<1) | 6 (1) |
BMI, body mass index; SD, standard deviation. aTaurolidine/heparin, n=401; heparin, n=402. bTaurolidine/heparin, n=403; heparin, n=402. cThe classification of participants as “Other” was due to site staff data entry errors. Catheter location (jugular or subclavian) for these participants was confirmed after data entry and documented in study records. | ||
Speak with a representative
Have questions about DefenCath? Open the form below to request a call with a representative.
Open formIMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION (cont'd)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
DefenCath is contraindicated in patients with:
- Known heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT).
- Known hypersensitivity to taurolidine, heparin or the citrate excipient (components of DefenCath), or pork products.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT): HIT was reported in patients using heparin, a component of DefenCath, as a catheter lock solution. If HIT occurs, discontinue DefenCath and institute appropriate supportive measures.
- Drug Hypersensitivity: Drug hypersensitivity reactions have been reported in patients using heparin, a component of DefenCath, as a catheter lock solution. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue DefenCath and institute appropriate supportive measures.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most frequently reported adverse reactions occurring in ≥2% of patients using DefenCath as a CLS were hemodialysis catheter malfunction, hemorrhage/bleeding, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, musculoskeletal chest pain, and thrombocytopenia.
Indications and Usage
LIMITED POPULATION: DefenCath® is indicated to reduce the incidence of catheter-related bloodstream infections (CRBSI) in adult patients with kidney failure receiving chronic hemodialysis (HD) through a central venous catheter (CVC). This drug is indicated for use in a limited and specific population of patients.
Limitations of Use
The safety and effectiveness of DefenCath have not been established for use in populations other than adult patients with kidney failure receiving chronic HD through a CVC.
Please see the full Prescribing Information.